Hence, the delay is five to eight yearsJakarta (ANTARA) - Pulmonology and Respiratory Medicine Professor, Faculty of Medicine, University of Indonesia (FKUI), Prof. Tjandra Yoga Aditama stated at the World Tuberculosis Day commemoration that COVID-19 majorly impacted the development of tuberculosis control globally, including Indonesia.
Aditama pointed to the huge impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on tuberculosis control efforts. Modeling by the Stop TB Partnership and Imperial College, Avenir Health, Johns Hopkins University and USAID estimates that disruption caused by the COVID-19 pandemic could make indicators of progress in the world's tuberculosis program regress to the situation in 2013-2016.
"Hence, the delay is five to eight years," Aditama noted in a written statement on Wednesday.
Another publication states that global tuberculosis detection decreases by an average of 25 percent in three months, so the number of deaths from tuberculosis will increase by 190 thousand. It translates to an additional 100 thousand deaths in the Southeast Asian region.
"If in 2018, there were 1.49 million deaths due to tuberculosis in the world, then due to the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, there could be 1.85 million deaths in the world," Aditama remarked.
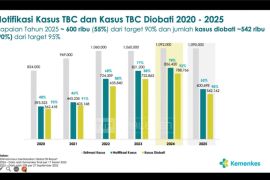
In fact, tuberculosis control in Southeast Asia, including in Indonesia, initially went quite well. One of the indicators is shown by the number of tuberculosis case notifications, which rose, from 2.6 million in 2015 to 3.36 million in 2018, or an increase of around 20 percent.
Meanwhile, the success of treatment for drug-sensitive tuberculosis also increased, from 79 percent in the 2014 cohort to 83 percent in the 2017 cohort.
Moreover, on the basis of the number of deaths, data indicates a decrease, from 758 thousand in 2015 to 658 thousand in 2018.
Such progress is expected to continue into 2020. However, the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 has limited the progress.
Aditama highlighted the two crucial steps of passive case finding at health facilities and active identification by health workers.
Such steps are in line with the seven activities that can be pursued along with the COVID-19 control efforts that comprise testing, contact tracing, infection prevention control, surveillance, strengthening health services, risk communication, and community involvement.
Aditama noted that it was not too late to apply the strategy to prioritize case detection and handling efforts, so that the death rate from tuberculosis does not increase.
Related news: COVID-19: Jakarta extends micro-scale activity restrictions
Related news: 5,533,379 Indonesians have been vaccinated against COVID-19
Close
EDITED BY INE
Translator: Lia Wanadriani Santosa, Katria
Editor: Fardah Assegaf
Copyright © ANTARA 2021