We cannot let more people contract diabetes.Jakarta (ANTARA) - The government is preparing strategies to prevent obesity in children to suppress the risk of non-communicable diseases, such as diabetes, the director of non-communicable disease handling and prevention at the Health Ministry, Eva Susanti, has informed.
"In the future, there will be an obesity national action plan. There will be a strategy undertaken by different ministries to implement prevention toward children," she said here on Thursday.
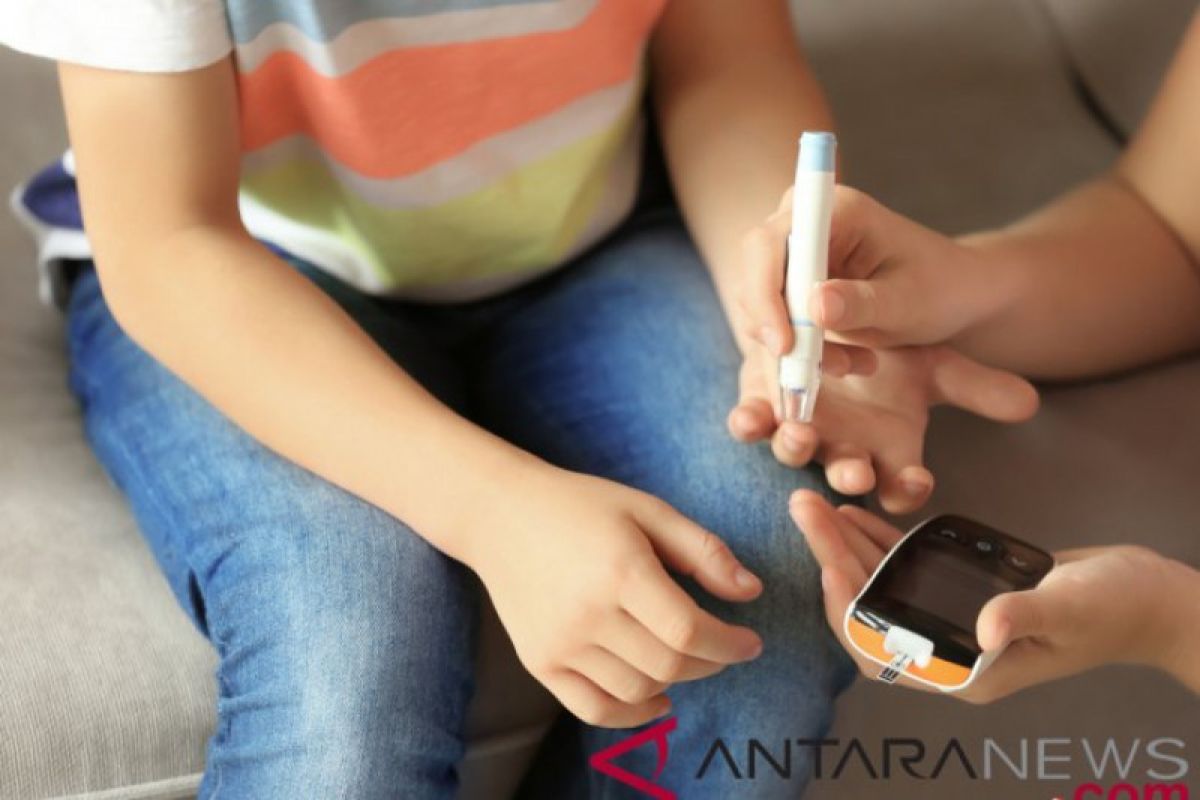
One of the most frequent non-communicable diseases in Indonesia is diabetes.
Diabetes is one of the diseases that still poses a burden to healthcare since it affects at least 537 million people worldwide. This figure is estimated to increase to 783 million by 2045, she informed.
Related news: Govt aims to improve mother-child health service at vertical hospitals
In Indonesia, the number of diabetes patients has continued to rise from 10.7 million in 2019 to 19.5 million in 2021. Moreover, this figure is estimated to rise to 28.6 million by 2045.
Indonesia is ranking fifth in terms of the number of diabetes patients in the world.
"This condition is driven by many factors, including contemporary lifestyle with frequent consumption of foods and beverages with excessive sugar content and lack of exercise, which increases the risk of diabetes," she explained.
Excessive consumption of sugar without physical activity can trigger obesity, which can lead to a variety of diseases and even death. This phenomenon will affect the productive age population in Indonesia, she said.
Related news: Support from IsDB to strengthen referral health services: Minister
"We cannot let more people contract diabetes," Susanti stressed.
Diabetes mitigation necessitates comprehensive efforts from all strata of society, she said.
The Health Ministry is committed to conducting health transformation, specifically in primary and referral services.
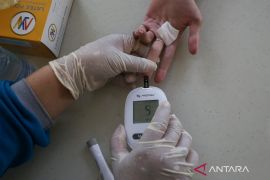
Primary service transformation is being undertaken by promoting a change in lifestyle through education, encouraging people to maintain eating patterns and conduct physical activities, and carrying out early detection of diabetes risk factors at health facilities.
Primary health services are being improved through the development of a practical guideline so that patients who have been detected early can receive medication based on the prevailing standards and their condition.
Meanwhile, referral service transformation is being undertaken by formulating a national referral network program.
Related news: Minister Hartarto suggests two policy focuses at APEC meeting
Related news: No additional acute kidney failure cases recorded in past fortnight
Translator: Nanien Yuniar, Fadhli Ruhman
Editor: Fardah Assegaf
Copyright © ANTARA 2022










![More Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Reach HbA[1c] Target with Apidra(R) on top of Lantus(R)](https://img.antaranews.com/cache/270x180/no-image.jpg)