The digital economy and finance will continue to increase very quickly to support our economic recoveryJakarta (ANTARA) - The COVID-19 pandemic has greatly affected the economies of various countries in the world, including that of Indonesia.
The pandemic that struck at the start of 2020 has had an impact on the economy of households; micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs); corporations; as well as other economic actors.
However, Indonesia has continued to make improvements in terms of bringing its COVID-19 pandemic situation under control.
Indonesia recorded just 216 positive cases in December 2021, a significant improvement as compared to July 2021, when the second wave of COVID-19 infections almost overwhelmed the country.
Indonesia has also registered a steady increase in the vaccination rate, with around 152.6 million, or 73.4 percent of the target population receiving the first vaccine dose.
Related news: Jakarta is Indonesia's economic hub: BI Governor
Apart from an increase in the vaccination rate, various economic recovery policies are already on the right track, so that the Indonesian economy can grow positively.
Coordinating Minister for Economic Affairs Airlangga Hartarto expects the country’s economic growth in the fourth quarter of 2021 to lie in the range of around 3.7 and four percent.
Hartarto noted that some key sectors, such as manufacturing, mining, and plantations, have recovered early. Meanwhile, the agriculture and real estate sectors have also shown resilience during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The minister remarked that the COVID-19 pandemic has posed major challenges in terms of the rising unemployment. In August 2020, the pandemic resulted in around 29.12 million people, or 14.28 percent of the working age population being categorized as unemployed, not working temporarily, not entering the workforce, and working with reduced hours.
Related news: No one to be left behind in COVID recovery: Hartarto
In order to overcome these problems, he noted, one of the strategies adopted was to utilize the Pre-Employment Card Program.
This program is immensely beneficial in improving the competence of the workforce through online vocational training. Another objective of this program is to maintain the purchasing power of the affected people through social assistance.
Recipients of the Pre-Employment Card Program are generally young workers aged 18 to 35 years and with high school level education or below.
Hartarto noted that the Pre-Employment Card also covers all community groups, including women, who have more than one dependent child in disadvantaged areas.
Until the end of November 2021, there were at least 78 million online registrants for the Pre-Employment Card Program. Meanwhile, since 2020, the number of beneficiaries had reached 11.4 million people, with total incentive disbursed amounting to Rp25.1 trillion.
Related news: Realisation of national recovery programme reaches Rp533.6 trillion
In terms of economic recovery, an evaluation survey of the Pre-Employment Card Program showed that after being registered and participating in this program, the number of unemployed beneficiaries decreased, from 56 percent to 39.8 percent.
In addition, the incentives received after the training is completed also increased the purchasing power as well as created jobs and entrepreneurship through MSMEs.
For MSMEs affected by the COVID-19 pandemic, he noted, the government had launched various policy programs to support and empower MSMEs in order to survive in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic.
A series of social protection programs have also been implemented by the government, including the Smart Indonesia Card for higher education, Smart Indonesia Program, national health insurance for contribution assistance recipients, Family Hope Program, cash social transfer, and staple food cards.
In addition to the COVID-19 pandemic, Hartarto noted, the Indonesian government views food security as one of the important issues that must be addressed in order to ensure a sustainable and resilient economy.
The government has established a national food system to increase food production and productivity to meet the national needs.
The system aims to fulfil five important objectives comprising sustainable domestic production and availability to meet the demand for quality and safe food, a conducive environment for local food development, stabilization of food access, strengthening farmer corporations and food distribution efficiency, as well as food assistance for households to address food insecurity.
Technology should be applied in production, distribution, and consumption to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of each process in producing food.
Indonesia's priority programs in the agricultural sector include price stabilization, integrated livestock, agricultural intensification, and controlled land conversion.
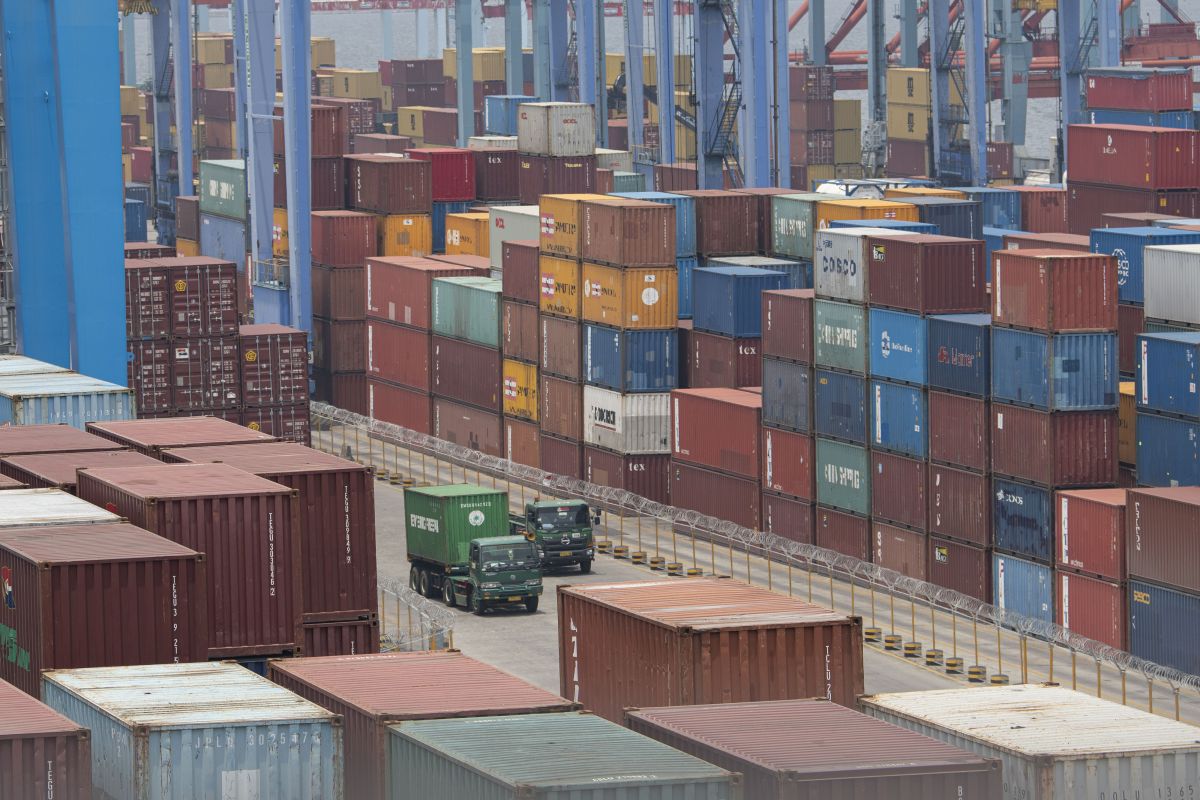
Meanwhile, the digital economy in Indonesia has continued to increase, Hartarto stated. In 2020, as much as 41.9 percent of the total ASEAN digital economy transactions came from Indonesia, which were contributed by the e-commerce sector, he pointed out.
Indonesia's total digital economy transactions had reached US$44 billion in 2020 and are expected to increase to US$124 billion by 2025, he added.
E-commerce transactions, digital banking, and electronic money are also forecast to continue to increase this year, he remarked. The largest increase of 48.4 percent (yoy) is expected in e-commerce transactions, he noted. Electronic money and digital banking are projected to increase by 35.7 percent (yoy) and 30.1 percent (yoy), he added.
"This increase in digital transactions has a crucial role and contributes to Indonesia's economic recovery during the COVID-19 pandemic," Hartarto stated.
Related news: Indonesia's G20 presidency boosts global investor confidence: Hartarto
Better prospects
Governor of Bank Indonesia (BI) Perry Warjiyo forecasts better prospects of economic recovery in 2022 as compared to 2021, with growth in the 4.7-5.5 percent range.
"Our economy will be better while heading towards recovery, with growth in the range of 4.7-5.5 percent in 2022, from this year's 3.2-4 percent," Warjiyo stated.
According to Warjiyo, the optimism of recovery must be strengthened by applying the precautionary principle. Growth was supported by development in the consumption, investment, export sectors as well as controlled inflation at three percent, give or take one percent.
"The digital economy and finance will continue to increase very quickly to support our economic recovery," he affirmed.
Related news: Controlling pandemic key to economic recovery: Hartarto
In addition, BI has responded to the precautionary principle through the synergy of existing national economic policies and was further strengthened by the Financial System Stability Committee (KSSK) and all stakeholders, including Commission XI of the House of Representatives.
"There is one prerequisite that we must follow together, which is expediting vaccination, so that mass immunity can be achieved immediately and open up economic sectors gradually to support the nation's economic recovery," he explained.
Warjiyo noted that the five policy responses of BI comprised the transformation of the real sector, including the downstreaming of natural resources, which also responded to global challenges to the green economy.
Second, the synergy between the Ministry of Finance and BI regarding fiscal and monetary policies in order to maintain macroeconomic stability and jointly restore the economy.
Third, BI, along with KSSK, encouraged credit and financing from the financial sector banking to the real sector of the business world, from the demand and supply side.
Related news: Indonesia rebound from pandemic quicker than 97-98 crisis: Indrawati
The fourth response is the digitalization of the national financial economy in accordance with President Jokowi's direction and the last policy response is developing and building an inclusive and green financial economy.
"That is our answer to prudence in an effort to ensure the prospects of economic recovery will rise and recover. Synergy and innovation in national economic recovery," he noted.
BI's policy in 2022 is focused on continuing to encourage economic recovery with synergies among the government, KSSK, and related stakeholders.
"The monetary policy is aimed at responding to the increasing global uncertainty," he expounded.
In addition, BI remains committed to maintaining exchange rate stability and ensuring better liquidity in the banking system.
BI has also planned to gradually and cautiously reduce banking liquidity assistance.
Thereafter, the low interest rate of 3.5 percent will continue to be maintained until there are signs of an increase in inflation.
Related news: International support helps boost domestic economic recovery: Hartarto
Related news: Social assistance has huge role amid pandemic: economist
Editor: Fardah Assegaf
Copyright © ANTARA 2021