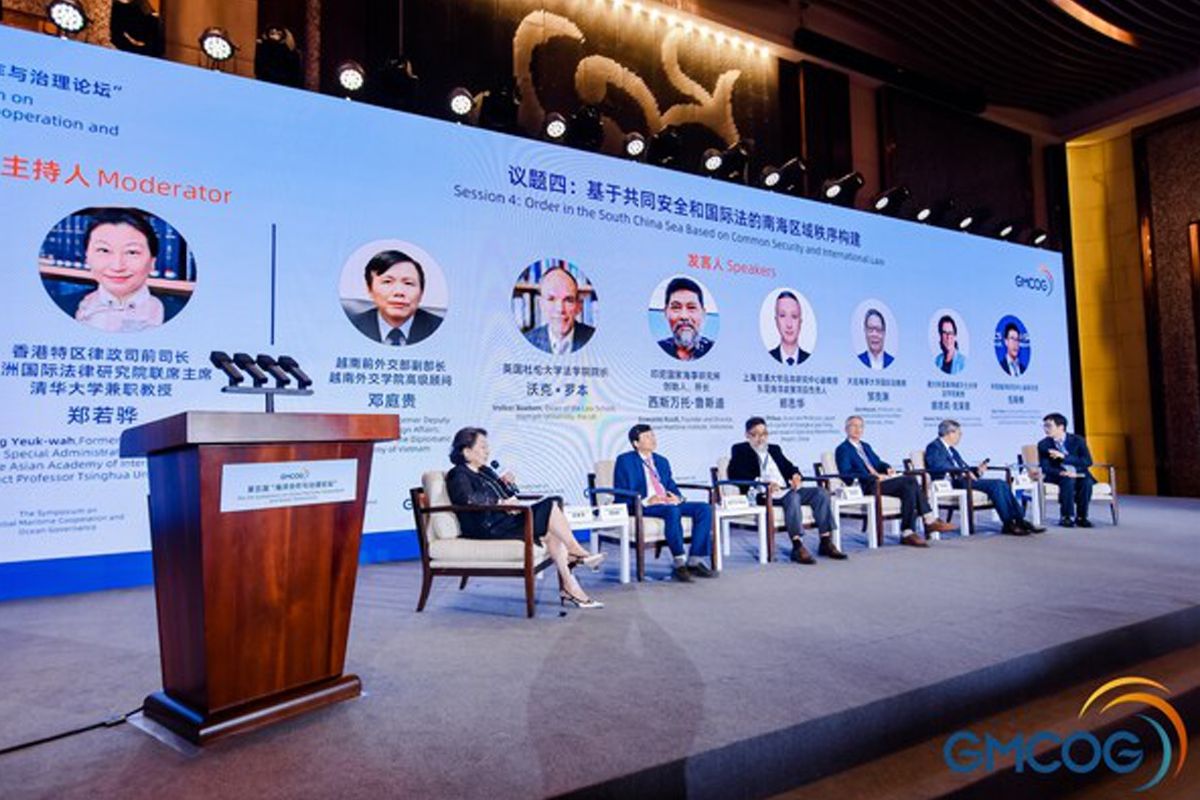
Zheng Zhihua, Associate Professor of Japan Research Center of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, pointed out that most countries in the South Pacific have completed maritime boundary delimitation based on regional commonalities, with numerous practices involving claims of exclusive economic zones (EEZs) and continental shelves based on coral reefs. The United States, France, and the United Kingdom also have similar practices in the South Pacific. These practices related to maritime rights claims can serve as a reference for the South China Sea region.
Zou Keyuan, Professor of Law School of Dalian Maritime University, China pointed out that there are various ways to resolve disputes, and legal means are only one of the available options. The diverse cultural differences in East Asia have resulted in the absence of a regional legal dispute resolution mechanism in the Asia-Pacific region to date. Therefore, it is not advisable to overly emphasize legal methods to resolve the South China Sea dispute.
Natalie Klein, Professor of Faculty of Law, University of New South Wales, Australia, outlined specific rules related to the freedom of navigation, including those concerning territorial seas and the high seas, and attempted to explain the meaning and scope of freedom of navigation.
SOURCE National Institute for South China Sea Studies, China
Reporter: PR Wire
Editor: PR Wire
Copyright © ANTARA 2024