On the other hand, imagine yourself sailing in a calm ocean. I am sure you will be able to predict when the ship will arrive at its destination with ease.
From this point, we can learn a few things. First, instability will lead to uncertainty. Uncertainty will make it difficult for us to predict the situation.
Second, instability will lower our expectations of the goals we want to achieve. This condition not only applies to the case above but also to more complex aspects, for example, the Indonesian economy.
All economic policies aim to create prosperity and distribute it to all people as economic actors. However, making the right economic policy is challenging.
Moreover, these policies must be taken in the midst of global economic instability. For example, who could have predicted 10 years ago that there would be a COVID-19 pandemic in 2020?
The condition that brought some countries to the brink of recession and others experiencing a slowdown in economic growth is one form of economic instability we have faced.
Keynesian Economics
We cannot avoid the various phenomena that cause economic instability. However, we can still mitigate them and respond appropriately.
Referring to Keynesian Economics, the government has a role in increasing aggregate demand, employment, and wealth redistribution.
According to the Keynesian view, the government can intervene in the economy through government spending policies.
This is believed to increase aggregate demand and, on the other hand, will also create jobs due to the increased demand for labor as a factor of production.
Keynesian Economics was chosen by many countries as a remedy to overcome the sluggish economy, and Indonesia is no exception. If we pay attention, Indonesia has disbursed a large amount of government spending every year.
The government spent Rp2,786.4 trillion in 2021 and Rp3,090.8 trillion in 2022 for government spending. When compared to Indonesia's gross domestic product of Rp16,976.6 trillion in 2021 and Rp19,588.4 in 2022, government spending has contributed more than 15 percent.
How can the government realize this considerable amount of government spending? Of course, this can only be done with an adequate source of funding. Yes, one of the answers is because of the taxes we pay.
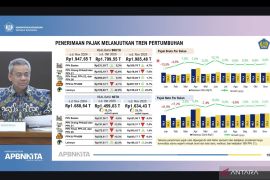
In 2021, the government collected tax revenue of Rp1,278.6 trillion and increased it to Rp1,716.8 in 2022. From this data, we can say that tax revenue is one of the crucial factors for realizing government spending.
Taxes, a critical component in implementing the state budget, have indirectly played a role in realizing economic stability and equitable distribution of welfare.
Economic stability can be measured through macroprudential indicators, such as economic growth rates, exchange rate fluctuations, and interest rate fluctuations (Rusydiana, 2019).
The economy is stable if macroprudential indicators show positive results and do not fluctuate too much. Then, how does tax play its role?
Not just a source of income
Taxes have two main functions: budgetary and regulated. In the budgetary function, taxes act as a source of funding to finance government spending.
In the regulated function, tax acts as an instrument to direct and regulate the course of the economy through taxation policies. These two functions run simultaneously and will affect the national economy.
Talking about the national economy, let us take a peek at economic growth. Economic growth is often used as the main indicator in assessing a country's economy.
One approach that is usually used to calculate the gross domestic product is the expenditure approach.
Through this approach, the gross domestic product is calculated from the sum of household consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports, or exports minus imports.
Hence, we can say that government spending has a hand in determining the level of economic growth.
Taxes play a crucial role in ensuring the availability of funding for various government expenditures. Government spending, both physical and programmatic, will have a multiplier effect on the economy, for example, the construction of roads and ports.
In their construction, these projects will create job opportunities and absorb labor. Once the projects are completed, the community will benefit from increased effectiveness and efficiency in the distribution of goods.
Of course, this will reduce freight costs, which in turn can reduce the price of goods and increase the people's purchasing power.
In times of economic instability, taxes also contribute to national economic recovery. The government has disbursed Rp540.7 trillion in tax incentives for workers, the industrial sector, and MSMEs during the COVID-19 pandemic in the 2020-2021 period.
Taxes have also contributed to accelerating the handling of COVID-19 by providing incentives in the form of tax exemptions for goods needed in handling the disease. This is an example that tax does not only aim to collect state revenue but also becomes a government instrument to stabilize economic conditions, so that the Indonesian economy might avoid recession and is able to rise in a relatively short period of time.
When it comes to equalizing welfare, taxes play a vital role. Taxes, especially income tax, are levied by taking into account the circumstances of each individual.
The government provides income tax exemptions for individual workers, who earn Rp54 million to Rp72 million a year, depending on the number of dependents they have. The government also waives taxes for individual MSME players, with a turnover of up to Rp500 million in a year.
Not only does it impose a non-taxable income, but in order to redistribute income, the government also applies a progressive tax rate. This means that the greater the income earned, the greater the tax paid, and vice versa; the lesser the income, the smaller the tax.
Currently, the government applies several layers of tax rates, ranging from five percent to 35 percent. This income redistribution is expected to be a solution to increase the purchasing power of low-income individuals and, at the same time, maintain the level of tax revenue from the contribution of the super-rich.
The ultimate goals
At the end of the day, the main objective of economic policy is neither to achieve the highest possible economic growth nor to collect as much tax and implement as much development as possible, but rather, to ensure that people live in prosperity and well-being.
The government is like a chef, who must ensure that the economic pie is served on the table every day and ensure that everyone, who sits at the table, gets a fair share. Of course, this is not an easy task.
Hence, everyone must understand and participate to create a stable economy and a prosperous society.
*) The author is the staff of the Ministry of Finance.
The views and opinions expressed on this page are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the ANTARA News Agency or the author's institution.
Related news: Finance Ministry should optimize taxes to boost state revenue: MPR
Related news: 2024 tax policy direction optimized through core tax system: Minister
Related news: Diligent taxpayers will help invest in education: Ministry
Copyright © ANTARA 2023