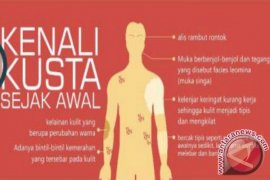
PARIS, Dec. 6 (ANTARA/ PRNewswire-AsiaNet) --
Two studies presented at World Diabetes Congress 2011 provide further evidence of the benefits to patients of early glycemic control on co-morbidities
Sanofi (EURONEXT: SAN and NYSE: SNY) announced today new results from sub-analyses of the First Basal INsulin Evaluation in Asia (FINE Asia) Registry study,[1] and the Cardiovascular Risk Evaluation in People with Type 2 Diabetes on Insulin Therapy (CREDIT) study.[2]
FINE Asia was a six-month, 11-Asian-country prospective observational study to assess the effect of 'time to basal insulin initiation' on glycemic control and co-morbidities in insulin-naïve adults with type 2 diabetes (T2D), uncontrolled on oral antidiabetic medications. Patients (n=2,673) were grouped according to duration of diabetes since diagnosis (<6y; 6-11y; or greater than or equal to12y). Results showed that people with T2D who are initiated on insulin therapy earlier in the progression of their diabetes achieved greater glycemic control.
Across the FINE Asia sub-analysis groups, baseline HbA1c was similar (9.8%), and the patients who had the shortest time to insulin initiation (71-79% insulin glargine users) showed the greatest (mean) improvement in HbA1c at 6 months: <6y: 7.5%; 6-11y: 7.8%; greater than or equal to12y: 7.9% (p<0.001 for all three groups).
Likewise, the percentage of patients reaching the target goal (HbA1c<7%) was less with increasing disease duration; those who had diabetes for less than 6 years were significantly more likely to achieve target HbA1c than those who had the disease for over 12 years: <6y: 53.4%; 6-11y: 39.5%; greater than or equal to12y: 32.8% (p<0.001 for all three groups). The percentage of patients experiencing hypoglycemic events was similar across groups.
Patients whose disease duration was relatively shorter experienced a significantly lower incidence of several co-morbidities, including retinopathy, neuropathy, nephropathy, coronary artery disease, hypertension and dyslipidemia. Early initiation of insulin therapy was associated with a reduction of diabetes-related complications, as well as other common co-morbidities. The levels of improvement following six months of basal insulin therapy varied with the number of years since disease diagnosis. The FINE Asia sub-analysis was not part of the original study protocol.
These results are supported by recent findings from a one-year real-life study of Cardiovascular Risk Evaluation in People with Type 2 Diabetes on Insulin Therapy (CREDIT), an international, multicenter observational study designed to assess the metabolic and diabetes parameters of people with T2D on long-term insulin therapy.
Results from a Japanese sub-analysis indicated that early initiation of insulin resulted in better glycemic control (HbA1c: 10.7% vs 7.9%; fasting plasma glucose [FPG]: 12.1mmol/l vs 7.7mmol/l; post-prandial glucose [PPG]: 16.5mmol/l vs 9.9mmol/l, p<0.001), with a low incidence of severe hypoglycemia and improved cardiovascular (CV) risk parameters at one year. The results from CREDIT are in line with the FINE Asia sub-analysis in supporting early insulin initiation in order to improve glycemic control and CV risk profile in people with type 2 diabetes.
"The results of the FINE Asiasub-analysis, as supported by the CREDIT 1-year Japanese study,indicate that in Asian people with type 2 diabetes, early treatment with insulin may be associated withsignificant improvements in glycemic control. Most importantly, early glycemic control may lead to significant improvement in cardiovascular risk parameters and reduction inthe incidence of co-morbidities," said Riccardo Perfetti, Vice President, Medical Affairs, Sanofi Diabetes.
Both the FINE Asia sub-analysis and the 1-year follow-up of the CREDIT study are presented today at the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) World Diabetes Congress, Dubai.
References
1: Variation of Glycemic Control and Patient Comorbidities With Duration of Type 2 Diabetes in Asian Patients: Analysis of the FINE Asia Registry. IDF/WDC 2011 Poster P-1455.
2: Baseline and 1-year interim follow-up assessment of Japanese patients initiating insulin therapy enrolled in the CREDIT study. IDF/WDC 2011 Poster P-1426.
About Sanofi Diabetes
Sanofi strives to help people manage the complex challenge of diabetes by delivering innovative, integrated and personalized solutions. Driven by valuable insights that come from listening to and engaging with people living with diabetes, the Company is forming partnerships to offer diagnostics, therapies, services, and devices. Sanofi markets both injectable and oral medications for people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Investigational compounds in the pipeline include an injectable GLP-1 agonist being studied as a single agent, in combination with basal insulin, and/or in combination with oral antidiabetic agents.
About Sanofi
Sanofi, a global and diversified healthcare leader, discovers, develops and distributes therapeutic solutions focused on patients' needs. Sanofi has core strengths in the field of healthcare with seven growth platforms: diabetes solutions, human vaccines, innovative drugs, rare diseases, consumer healthcare, emerging markets and animal health. Sanofi is listed in Paris (EURONEXT: SAN) and in New York (NYSE: SNY).
Forward Looking Statements
This press release contains forward-looking statements as defined in the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, as amended. Forward-looking statements are statements that are not historical facts. These statements include projections and estimates and their underlying assumptions, statements regarding plans, objectives, intentions and expectations with respect to future financial results, events, operations, services, product development and potential, and statements regarding future performance. Forward-looking statements are generally identified by the words "expects", "anticipates", "believes", "intends", "estimates", "plans" and similar expressions. Although Sanofi's management believes that the expectations reflected in such forward-looking statements are reasonable, investors are cautioned that forward-looking information and statements are subject to various risks and uncertainties, many of which are difficult to predict and generally beyond the control of Sanofi, that could cause actual results and developments to differ materially from those expressed in, or implied or projected by, the forward-looking information and statements. These risks and uncertainties include among other things, the uncertainties inherent in research and development, future clinical data and analysis, including post marketing, decisions by regulatory authorities, such as the FDA or the EMA, regarding whether and when to approve any drug, device or biological application that may be filed for any such product candidates as well as their decisions regarding labeling and other matters that could affect the availability or commercial potential of such products candidates, the absence of guarantee that the products candidates if approved will be commercially successful, the future approval and commercial success of therapeutic alternatives, the Group's ability to benefit from external growth opportunities as well as those discussed or identified in the public filings with the SEC and the AMF made by Sanofi, including those listed under "Risk Factors" and "Cautionary Statement Regarding Forward-Looking Statements" in Sanofi's annual report on Form 20-F for the year ended December 31, 2010. Other than as required by applicable law, Sanofi does not undertake any obligation to update or revise any forward-looking information or statements.
Contacts:
Corporate Media Relations Sanofi Diabetes Global Communications
Marisol Peron Tilmann Kiessling
Tel: +33(0)1-53-77-45-02 Mobile: +49(0)172-61-59-291
Mobile: +33(0)6-08-18-94-78 E-mail: Tilmann.Kiessling@sanofi.com
E-mail: Marisol.Peron@sanofi.com
Source: Sanofi
Editor: PR Wire
Copyright © ANTARA 2011