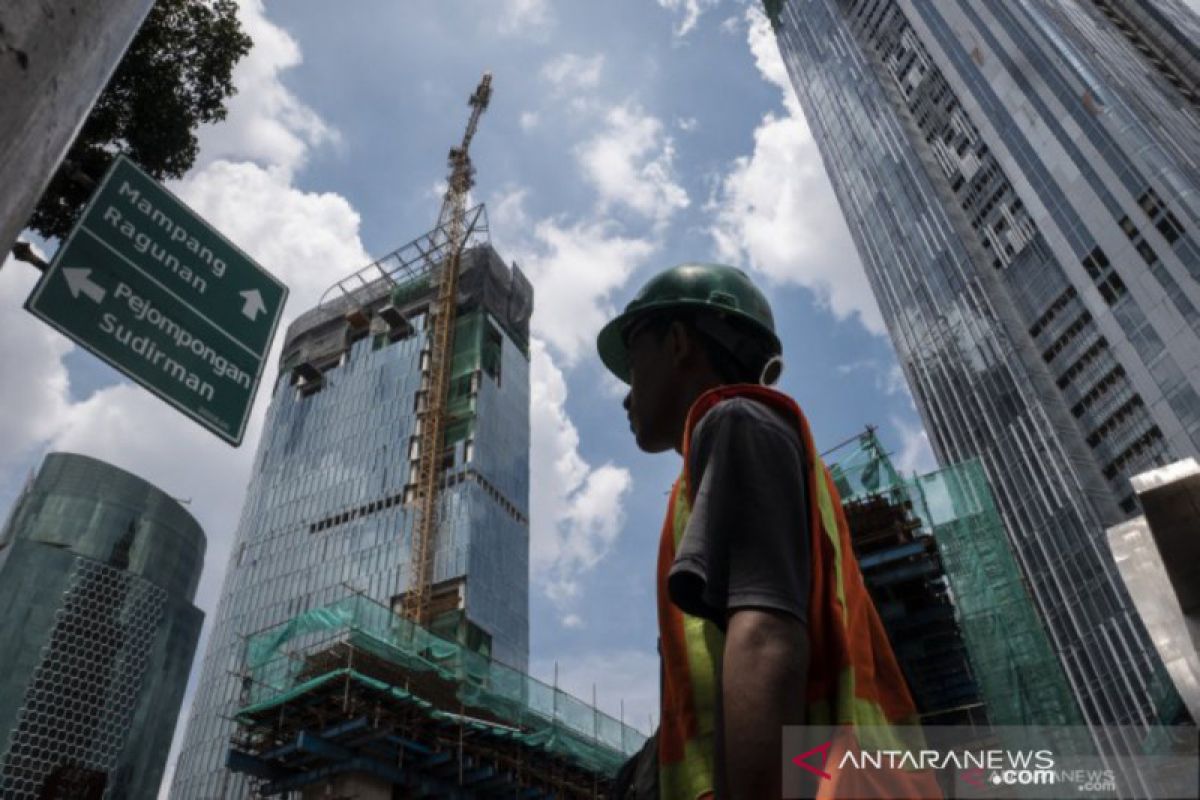
Our economy contracted 5.32 percent in the second quarter and 3.49 percent in the third quarter. This means it has passed its lowest point and is moving toward a positive trendJakarta (ANTARA) - The coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic that emerged earlier this year has significantly affected the state of the global economy.
The pandemic has impacted not only health but also the economy, thereby resulting in economic recession in countries.
Indonesia is on the list of nations to have recorded negative economic growth owing to COVID-19 that has led to an economic recession.
The Central Statistics Agency (BPS) reported that in the third quarter of 2020, Indonesia's economy recorded a -3.49 percent contraction year-on-year (yoy), better than -5.32 percent in the second quarter of 2020.
Negative economic growth recorded in the two quarters resulted in Indonesia entering into an economic recession, trailing behind other countries in the world.
However, Finance Minister Sri Mulyani Indrawati noted that economic growth in the third quarter of 2020 was quite good as compared to the position in the previous quarter.
This demonstrates that the process of economic recovery and a reversal of national economic activity is currently heading in a positive direction.
This is better than the previous quarter figure of -5.32 percent. All economic components, both in terms of expenditure and production, have increased, the minister remarked.
Meanwhile, President Joko Widodo (Jokowi) expressed belief that the Indonesian economy has passed its lowest point and is moving toward recovery.
Several macroeconomic indicators have shown signs of growth, including the import of raw materials and capital goods to support the processing industry.
The head of state also believed that Indonesia's trade surplus of US$8 billion in the third quarter of 2020 will contribute to maintaining the country's external economic resilience.
"Our economy contracted 5.32 percent in the second quarter and 3.49 percent in the third quarter. This means it has passed its lowest point and is moving toward a positive trend," he remarked.
Investors' confidence in the money market also continued to rise, as mirrored by the movement of the Composite Stock Price Index (IHSG) and strengthening of the rupiah's exchange rate in recent weeks, he stated.
"From the standpoint of the capital and financial markets, performance of the IHSG and the rupiah's exchange rate has risen to the tune of 5,522 and Rp14,050 per dollar respectively as of November 17, 2020. The improving performance of the IHSG was fueled by the rising index of sectoral stocks. The basic industry recorded the highest level of share index recovery after it plunged on March 24, 2020," he explained.
The positive momentum of the national economy must be maintained. However, while the economic recovery is underway, efforts to maintain public health in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic must be prioritized, he stated.
"We must remain cautious and disciplined in following health protocols while not becoming inattentive. Stay alert for a second wave of (COVID-19) that will have a detrimental impact on our efforts and sacrifices," he emphasized.
Prerequisite and five strategies
Bank Indonesia (BI) is optimistic that national economic recovery in 2021 would be realized by boosting synergies through a prerequisite and five strategies.
The prerequisite is vaccination coupled with disciplined adherence to the COVID-19 protocols, while the five policy response strategies are opening up productive and safe sectors, accelerating fiscal stimulus (budget realization), increasing credit from the demand and supply side, monetary stimulus and macroprudential policies, and digitalization of the economy and finance, especially MSMEs.
BI Governor Perry Warjiyo delivered these remarks at the 2020 Bank Indonesia Annual Meeting themed "Synergize to Build Optimism for Economic Recovery" held virtually on Thursday (Dec 3) in Jakarta.
The ongoing national economic recovery is projected to increase, Warjiyo stated.
In 2021, the Indonesian economy is forecast to grow and lie in the 4.8 percent - 5.8 percent range, supported by an increase in export performance, private and government consumption, as well as investment from both the Government capital expenditures and foreign investment as a positive response to the Job Creation Law.
Growth will also increase in all regions, especially in Java and the Sulawesi-Maluku-Papua region.
Macroeconomic stability will be maintained, with inflation under control, and targeted at three percent, give or take one percent, while the rupiah exchange rate will be stable, with the potential to strengthen.

Financial system stability will also increase, with high capital ratios, low NPLs, and growth in each third-party funds and credit that will rise to around seven to nine percent in 2021, Warjiyo stated.
The momentum for national economic recovery should be constantly encouraged by bolstering synergy to build optimism by all parties, including the central and regional governments, BI, the Financial Services Authority (Otoritas Jasa Keuangan, OJK), the Deposit Insurance Corporation (Lembaga Penjamin Simpanan, LPS), banks, and various other parties.
BI supports national economic recovery through the monetary policy stimulus that will be continued in 2021 that comprises stability of the rupiah exchange rate in line with fundamentals and maintained market mechanisms, interest rates that will remain low until signs of increasing inflationary pressure surface, and continued purchase of SBN from the primary market to finance the 2021 State Budget as a non-competitive bidder, and macroprudential policies that will remain accommodative in 2021.
Economic growth
Institute for Development of Economics and Finance (Indef) Deputy Director Eko Listiyanto forecast Indonesia's economic growth in 2021 at 2.5-three percent since the financial and real sectors were estimated to still operate at half capacity.
"If it is still half of the normal capacity, the government's target of five percent in 2021, cutting it in half by 2.5-3 percent is more realistic," Listiyanto stated.
Listiyanto believes several challenges will present themselves in 2021, including related to vaccination, which is expected to boost the economy, but uncertainty loomed large over the COVID-19 vaccination being conducted in the first semester.
The Indef deputy director explained that handling a pandemic was the key, especially in the path toward economic recovery.
Meanwhile, the 2020 inflation target is estimated to lie in the range of three percent and even below two percent.
Furthermore, he estimated that the realization of credit disbursement in 2021 would be choked up, and monetary expansion could not then be bigger since the rupiah was more volatile than other countries in the ASEAN.
"Hence, to reduce the fluctuating tensions, the interest rate should be set attractive, so that it cannot expand rapidly," he stated.
Even so, several indicators in the third quarter of 2020, including the Indonesian manufacturing index (PMI), began to improve, from 27.5 in March to 47.2 in September 2020.
Related news: Green economy takes precedence in push for recovery
Related news: Indonesia's economy has passed lowest point: President
Close
EDITED BY INE
Editor: Fardah Assegaf
Copyright © ANTARA 2020